Operational Risk: Key Risk Indicators (KRIs)
Key Risk Indicators Defined
Key Risk Indicators (KRIs) are an important tool within risk management and are used to enhance the monitoring and mitigation of risks and facilitate risk reporting. Operational risk is defined as the risk of loss resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes, people and systems or from external events. Operational KRIs are measures that enable the risk managers to identify potential losses before they happen; the metrics act as indicators of changes in the risk profile of a firm.
Effective KRIs
- Measurable – metrics should be quantifiable (e.g. number, count, percentage, dollar volume, etc)
- Predictable – provide early warning signals
- Comparable – to track over a period of time (trends)
- Informational – provide a measure of the status of the risk and control
Leading & Lagging KRIs
- Leading KRIs – are measures that are considered predictive in nature. They are derived from metrics that can help to forecast future occurrences
- Lagging KRIs – metrics based on historical measures. Help to identify trends in the firm
Importance of KRIs
KRIs play an important role in risk management by predicting potential High Risk areas and enabling timely action.
KRIs enable firms to:
- Identify current risk exposure and emerging risk trends
- Highlight control weaknesses and allow for the strengthening of poor controls
- Facilitate the risk reporting and escalation process
- Operational risk management adds value to the firm
Regulatory Expectations
To qualify to use the Advanced Measurement Approach (AMA) to calculate operational risk capital under Basel II, the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS) has specified detailed criteria for the use of forward looking measures. The choice of each factor needs to be justified as a meaningful driver of risk and whenever possible, the factors should be translatable into quantitative measures that lend themselves to verification. The sensitivity of a firms risk estimates to changes in the factors and the relative weighting of the various factors need to be well reasoned.
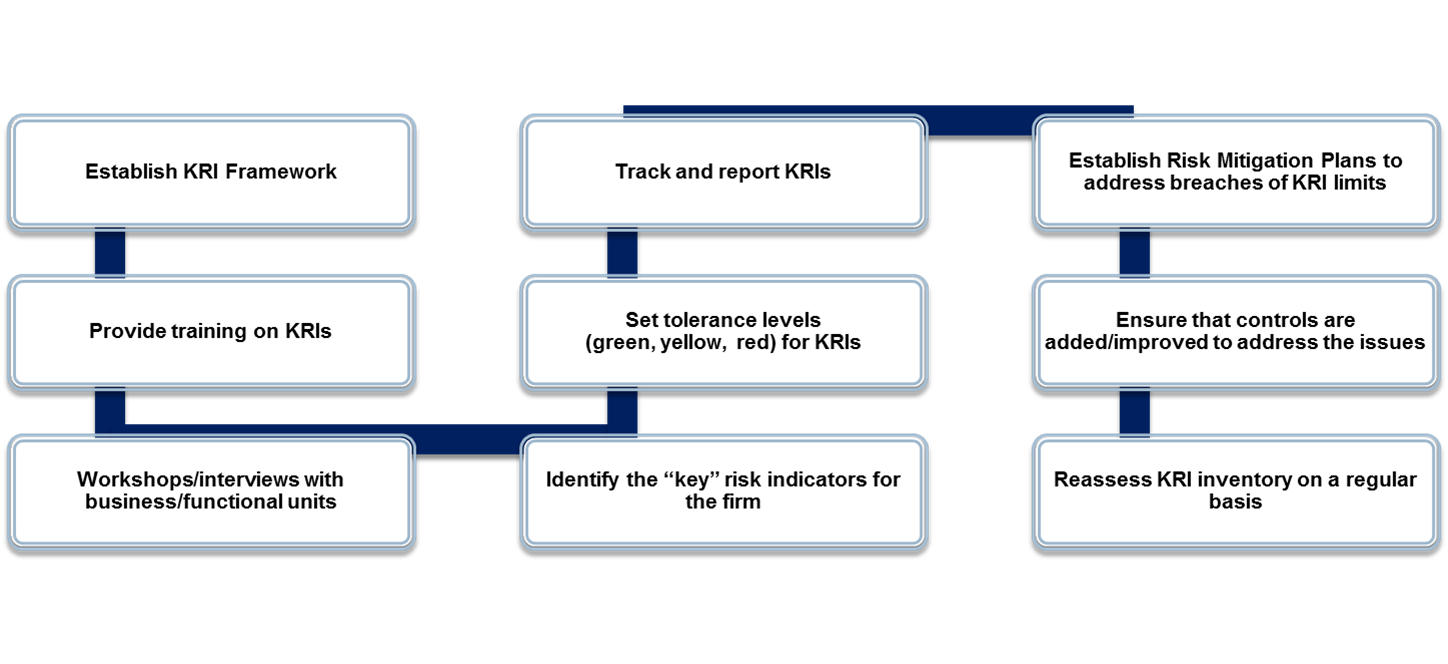
KRI Roadmap
Below is a high-level roadmap for establishing a KRI framework:
KRI Identification
- Identify existing metrics
- Assess gaps and improve metrics
- Identify KRIs via Risk Control Self-Assessment (RCSA) – (see ERM article for info) – interview business units
- Don’t over rely on them; focus on indicators which track changes in the risk profile or the effectiveness of the control environment
- Concentrate on the significant risks and their causes and consider forward looking and historical indicators
- Consider absolute values and numbers, ratios, percentages, ageing, etc
- Data on KRIs should be collated on a systematic and consistent basis in order to be meaningful, e.g. on a monthly basis.
KRI Selection
- Select the KRIs that are measurable, meaningful and predictive (leading indicators)
- Need a good mix of leading and lagging indicators for effective risk management
- Don’t select too many KRIs
- Too difficult to manage (track)
- Might become unmanageable
- Select only the ones that provide useful information
Setting Thresholds
- Determine and validate trigger levels or thresholds
- Based on industry tolerance or internal acceptance
- Board of Directors should approve thresholds
- Should coincide with risk appetite statement
KRI Tracking & Reporting
- Periodic tracking of KRIs (monthly, weekly, depends on what the KRI represents)
- KRIs should be reported regularly and escalation procedures should be in place (as part of the KRI framework) to ensure timely reporting to management and board
- Various KRIs will have different levels of escalation- when in doubt, escalate higher but don’t dump too much information on management/board- they will get overwhelmed
- Reporting of KRIs to Head of Business Units by KRI owners; Head of BU then reports into Risk Management; Risk Management reports to Risk Board and when applicable Full Board
- This can help improve Corporate Governance structure
Risk Mitigation Plans
- Risk Mitigation Plans (RMPs) should be set for High risk items
- Items with high severity or high frequency of occurrence need to have risk mitigation plans to mitigate risk and enhance controls
- Determine what is High risk by assessing control levels
- Track RMPs to ensure that controls are enhanced and risk is mitigated- report on RMPs to management/board and set target completion dates
Roles & Responsibilities
- Risk Management
- Create Framework and provide training
- Guidance and challenge KRI selection process
- Reporting/Escalation of breaches
- Identify Trends
- Business Units
- Identify KRIs
- Set thresholds
- Monitor positions
- Escalate breaches of limits to Management
- Internal Audit
- Validation and assurance around KRI process
- Incorporate output into Audit plan
- Assess control effectiveness for KRIs that were breached or yellow
Challenges
Potential challenges of establishing an effective KRI framework include:
- Getting business units to buy-in into the need for KRIs
- Demonstrating the effect (positive) that it can have on the firm overall and for each business unit
- Might result in setting aside more capital
- Identification of KRIs can prove to be difficult
- Lack of resources to track KRIs
IMPORTANT
Useful Links & Documents on Operational Risk KRIs

KSENIYA (KATE) STRACHNYI is an advisory consultant focused on risk management, governance, and regulatory response solutions for financial services institutions. Areas of expertise include governance frameworks, enterprise risk management programs, ICAAP, compliance risk management, operational risk management, Foreign Enhanced Prudential Standards, Basel II/III, and the Dodd-Frank Act.